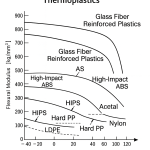
Acrylic vs. Polycarbonate – What’s the Difference?
Acrylic (PMMA) and Polycarbonate (PC) are two of the most widely used transparent engineering plastics. While they are often used in similar applications, such as panels, displays, and glazing, their material properties and performance differ significantly. Here’s a side-by-side comparison to help clarify the key distinctions.
Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate is extremely impact-resistant—about 250 times stronger than glass. It is often used in bullet-resistant glazing and industrial safety products.
Acrylic is less impact-resistant (about 10–20 times stronger than glass) but still suitable for most indoor and outdoor applications where extreme durability is not required.
Optical Clarity
Both materials offer excellent transparency (92%+ light transmittance). Acrylic typically has better optical clarity and gloss, making it ideal for display cases, signs, and decorative panels.
Polycarbonate may have slightly lower optical clarity but is more robust under stress and thermal conditions.
Heat Resistance
Polycarbonate withstands higher temperatures (up to ~120°C continuously), while acrylic softens around 80–90°C.
For applications requiring heat exposure or thermoforming, PC is the preferred choice.
Scratch Resistance
Acrylic has a naturally harder surface, making it more scratch-resistant than polycarbonate. However, PC can be coated with hard coats for improved abrasion resistance.
Workability
Acrylic is easier to cut, polish, and bond with solvents. It is more brittle but simpler to fabricate.
Polycarbonate can be cold-bent and drilled without cracking, and it excels in complex forming processes like insert molding and thermoforming.
Cost
Acrylic is generally more affordable than polycarbonate, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects where extreme durability is not essential.
Summary Table
| Property | Acrylic (PMMA) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | Very High |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent | Good |
| Heat Resistance | Low | High |
| Scratch Resistance | High | Low (unless coated) |
| Ease of Fabrication | Easy | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
In summary, choose acrylic when you need optical beauty, light weight, and cost-efficiency. Choose polycarbonate when strength, safety, and heat resistance are critical.